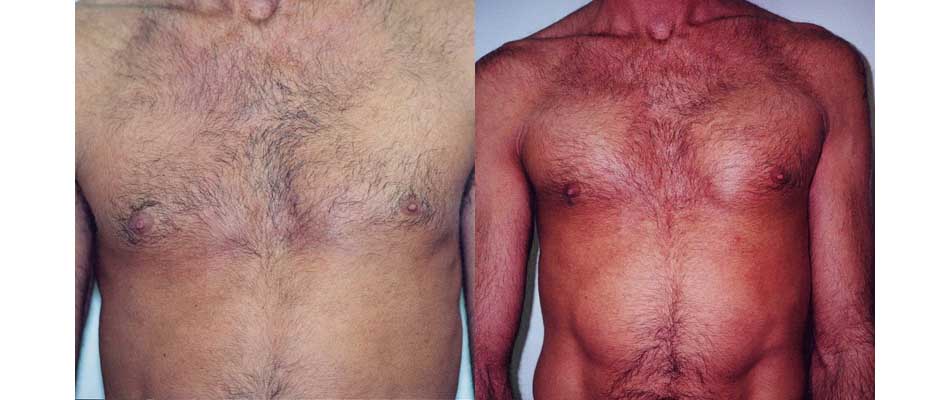
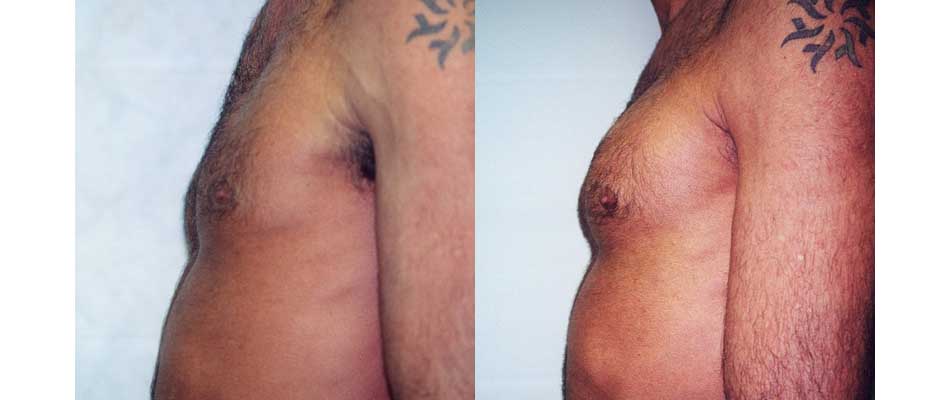
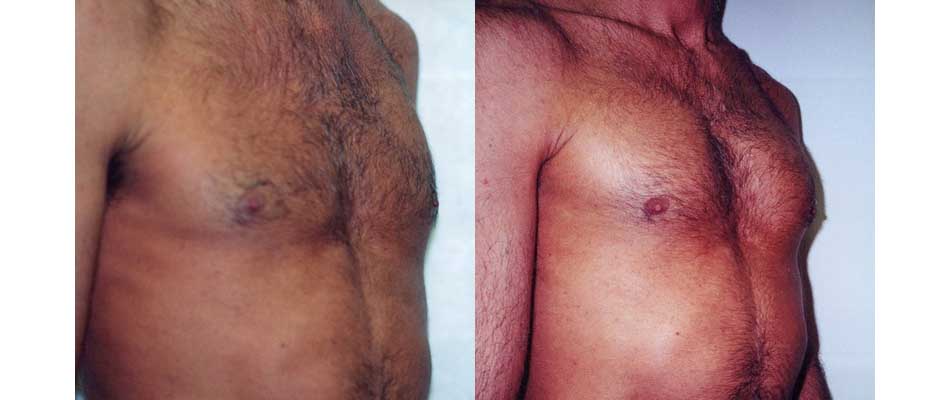
Pectoral Implants
Sometimes, no matter how much you work out, the toned, defined chest you’re working for just isn’t possible. And if you’re uncomfortable with how your chest looks, it can affect your self-confidence.
If you wish you could create a stronger-looking chest with better muscle definition, pectoral implant surgery (pectoral augmentation) may be an option. Pectoral implant surgery can give you a more muscular, sculpted-looking chest in just a few weeks.
Pectoral implant surgery can be used for cosmetic or reconstructive reasons, like:
- To enhance the chest when workouts haven’t produced satisfying results
- Reconstructive surgery after illness or traumatic injury
- Gender confirmation surgery
During the surgery, your plastic surgeon will place a soft silicone gel implant behind the pectoralis muscles to add depth and definition, creating a fitter, more sculpted look.
What are Pectoral Implants?
Pectoral implants are made of soft, FDA-approved silicone. The implants are placed under the pectoralis muscles to provide both bulk and shape. Unlike female breast implants, pectoral implants are solid, not filled.
A successful augmentation can increase the fullness and projection of the chest, giving you shape, volume, and symmetry.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Pectoral Implants?
As with any plastic surgery procedure, you should carefully consider the risks and benefits of pectoral implants, including your reasons for wanting implants. While pectoral implants can boost self-confidence, having the surgery to reflect someone else’s preferences may not.
Are you a good candidate for pectoral implants? You may be if you:
- Are unhappy with the size or contour of your chest
- Find that exercise has not developed your pectoralis muscles adequately
- Had a traumatic injury that affected the development or shape of your pectoralis muscles
- Have a congenital condition that affects your pectoralis muscles
- Have one or both pectoralis muscles that did not develop normally
- Would like a more symmetrical chest
- Are physically healthy
- Are fully developed
- Have realistic expectations
The Procedure
At your initial consultation, your doctor will review your medical history, complete a physical exam, take chest measurements, discuss your expectations, and go over the risks and benefits of surgery.
Before having surgery, your doctor may ask you to:
- Stop smoking
- Stop drinking alcohol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stop taking certain medications temporarily, especially blood thinners
- Arrange for help at home during your recovery
If you can’t work from home, you may need to take a week or two off while recovering.
Your procedure will be in an outpatient center or hospital under general anesthesia. On the day of your surgery, you should bring a friend or family member to drive you home. The procedure lasts about 1 to 1.5 hours.
During the procedure:
- Your chest will be shaved.
- Your surgeon will make small incisions in the armpit.
- Implants will be placed in a “pocket” created under the pectoralis muscle.
- The incisions will be closed with small stitches and adhesive or surgical tape.
- Your chest will be wrapped in a compression dressing to support the tissue while healing and to minimize swelling and bruising.
- You will rest in a recovery area until you are cleared to go home. Before leaving, your surgeon will talk to you about post-operative instructions and care.
Recovery
You may go home with pain medication, temporary drainage tubes, and a compression vest or wrap. You may need to wear a compression garment for up to six weeks.
For the first week or two after surgery, it’s common to experience symptoms like:
- Bruising
- Drainage at the incision site
- Inflammation
- Swelling
While recovering, you will need to avoid:
- Any manual labor
- Lifting
- Raising your arms over your head
- Wearing underarm deodorant for a week or two
- Working out
Before you go home, your care team will go over important post-procedure information, like:
- How and when to take pain meds
- How to care for your dressings and stitches
- Physical restrictions
- The best sleeping position to keep pressure off your chest
- What signs of infection or other complications you should watch for
- When you can return to normal activities
- Who to call with questions or concerns
- Your follow-up appointments
It is essential to your healing and to achieving your best results that you carefully follow all of the post-procedure instructions.
You should notice the change in the contour of your chest at once, but it can take a few months to completely heal and settle into your new shape.
Risks
Although pectoral implant surgery is safe and typically very successful, any surgery carries a risk of complications. Before scheduling pectoral implant surgery, you should carefully consider the risks and benefits. At your initial consultation, we’ll explain the risks and answer any questions you may have.
Complications are rare but could include:
- Asymmetry
- Bleeding
- Fluid buildup
- Hematoma
- Incorrect positioning
- Infection
- Muscle spasms in your upper arms
- Numbness
- Pain
- Poor scarring
- Reactions to anesthesia
- Tight scar tissue around the implant
How much do pectoral implants cost?
Most insurance plans don’t cover cosmetic procedures. The typical cost of pectoral implants varies by surgeon and is based on:
- The type of procedure used
- The skill and experience of your surgeon
- Geographic location
- Medical tests required
- Anesthesia
- Operating room costs
- Surgeon’s fee
- Prescriptions
- Compression garments for after surgery
Cost is an important factor for most people, but it’s essential to choose a surgeon you feel comfortable with when you’re deciding on plastic surgery. You’ll feel more at ease when you know you can trust your surgeon.